December 08 2005 4:01 PM EST
CONTACTAbout UsCAREER OPPORTUNITIESADVERTISE WITH USPRIVACY POLICYPRIVACY PREFERENCESTERMS OF USELEGAL NOTICE
© 2025 Equal Entertainment LLC.
All Rights reserved
All Rights reserved
By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
We need your help
Your support makes The Advocate's original LGBTQ+ reporting possible. Become a member today to help us continue this work.
Your support makes The Advocate's original LGBTQ+ reporting possible. Become a member today to help us continue this work.
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles's AIDS Institute report that they've discovered that each person's immune system responds to HIV in different ways--even the immune systems of identical twins. Writing in the December 5 edition of the Journal of Virology, the scientists said their findings show that the body's defenses against the virus are random rather than genetically determined.
The researchers followed the cases of male twins who were infected shortly after their 1983 births in Los Angeles by blood transfusions administered from the same donor at the same time. Infected with the same strain of the virus, the twins continue to live in the Los Angeles area and grew up exposed to the same environmental factors. Yet T-cell receptors (TCRs) reacted differently in each twin, showing that the body's defense response was random and unpredictable. TCRs play an important role in the immune system by binding to the receptors on the surfaces of viruses and then killing the invader. HIV escapes this action by changing shape so that it does not fit into those receptors.
"These boys are as similar as two humans can be, yet we see differences in how they fight the virus," said researcher and UCLA professor of pediatrics Paul Krogstad in a press release. "That's one more thing that makes it difficult to develop a vaccine for everyone."
When a virus invades a body, the cellular immune response targets small parts of proteins in the virus. This targeting mechanism itself is genetically determined, and the twins' targeting of HIV was remarkably similar, even 17 years after infection. But their overall TCR characteristics were highly divergent. This finding demonstrates that the interaction between their immune systems and the virus was random and unpredictable--indicating that a "one size fits all" vaccine may not be possible.
"If the goal is to develop a vaccine, our findings suggest this may not be so straightforward," said Otto Yang, associate professor of infectious diseases at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and the study's lead researcher, in a press release.
The UCLA researchers say the results of their study have broader implications, and could apply to other viruses such as cytomegalovirus, a herpes virus that causes opportunistic infections, and hepatitis C, the latter being similar to HIV in both its changeable and chronic nature. (Advocate.com)
From our Sponsors
Most Popular
Bizarre Epstein files reference to Trump, Putin, and oral sex with ‘Bubba’ draws scrutiny in Congress
November 14 2025 4:08 PM
True
Jeffrey Epstein’s brother says the ‘Bubba’ mentioned in Trump oral sex email is not Bill Clinton
November 16 2025 9:15 AM
True
Watch Now: Pride Today
Latest Stories
Rachel Maddow on standing up to government lies and her Walter Cronkite Award
December 15 2025 3:53 PM
Beloved gay 'General Hospital' star Anthony Geary dies at age 78
December 15 2025 2:07 PM
Rob Reiner deserves a place in queer TV history for Mike 'Meathead' Stivic in 'All in the Family'
December 15 2025 1:30 PM
Culver City elects first out gay mayor — and Elphaba helped celebrate
December 15 2025 1:08 PM
Texas city cancels 2026 Pride after local council rescinds LGBTQ+ protections
December 15 2025 12:55 PM
North Carolina county dissolves library board for refusing to toss book about a trans kid
December 15 2025 11:45 AM
Florida and Texas launch 'legal attack' in push to restrict abortion medication nationally
December 15 2025 11:18 AM
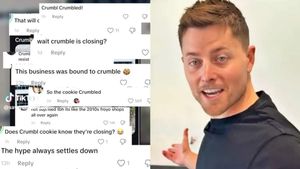
No, Crumbl is not Crumbl-ing, gay CEO Sawyer Hemsley says
December 15 2025 10:12 AM
11 times Donald Trump has randomly brought up his ‘transgender for everybody’ obsession
December 15 2025 9:22 AM
The story queer survivors aren't allowed to tell
December 15 2025 6:00 AM
Rob Reiner, filmmaker and marriage equality advocate, and wife Michele dead in apparent homicide
December 15 2025 1:08 AM
Trending stories
Recommended Stories for You


































































Charlie Kirk DID say stoning gay people was the 'perfect law' — and these other heinous quotes